
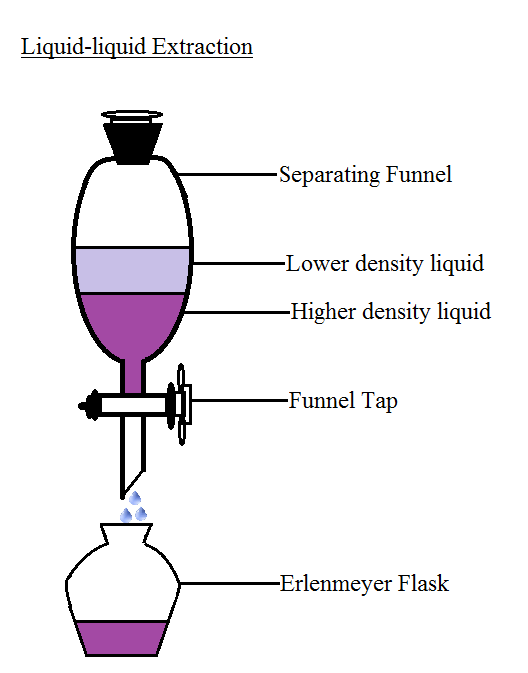
In liquid-liquid extraction, a solute is transferred from one liquid to another. First, in solid-liquid extraction, the solute is transferred from a solid phase to a liquid phase. Generally, there are three types of extractions. Extraction is also used to facilitate the isolation of a solute from a reaction solvent that is difficult to remove by evaporation, such as a solvent with a high boiling point. In the extraction process, a solute is transferred from one phase to another to separate it from unreacted starting materials or impurities. Then, you will perform an acid-base extraction to separate benzoic acid and caffeine.Įxtraction is a common technique used in organic chemistry to isolate a target compound. First, you will use extraction and filtration to isolate cellulose. In this lab, you will separate a mixture of cellulose, benzoic acid, and caffeine.
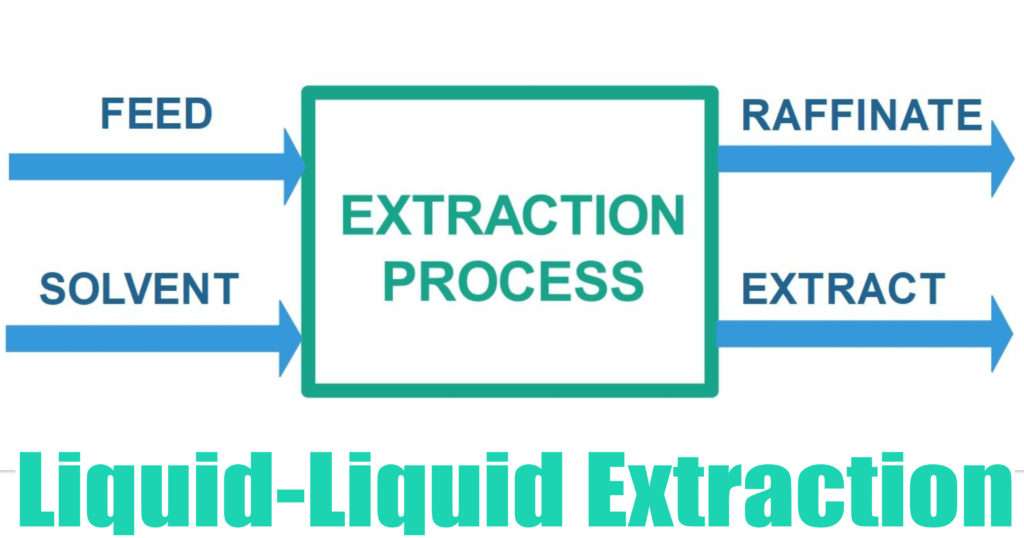
The ionic compound is collected and then either deprotonated or reprotonated to convert it back to its original compound. In both instances, the ionic compound will transfer to the aqueous phase, and the neutral compounds will partition to the organic phase. Conversely, adding an acid would transfer a proton to a basic compound. The base will accept a proton from the acidic compound, making it ionic. To separate acidic compounds, a base is added to the mixture. Recall that an acid is a compound that donates a proton when dissolved in water, and a base is a compound that accepts a proton. Keep in mind that it is likely that there will be residue of each component in both phases.Īn acid-base extraction is a special type of liquid-liquid extraction that separates acidic and basic compounds based on the solubility differences. Once the solutes have separated, the two different phases are collected. The partition coefficient, K, is the ratio of solute concentration in the organic phase to that in the aqueous phase. In general, non-polar solutes will partition into the organic phase, and polar solutes will partition into the aqueous phase. Therefore, it is important to choose solvents with different polarities. Then, each solute compound will transfer to the phase in which it is most soluble. Liquid-liquid extractions are performed in a separatory funnel so that the more dense solvent will settle to the bottom and the less dense solvent will sit on top. The solvents must be immiscible, meaning they do not mix and are separate phases. Liquid-liquid extraction is another type of extraction where the mixture is dissolved in two immiscible liquid phases. This is an example of a solid-liquid extraction.

Any time you steep tea, you're extracting water-soluble compounds, like caffeine and flavors, from the tea leaves into your hot water. You are already familiar with extraction. Extraction is a technique to separate components from a mixture.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
